US Pharm.
2008;33(12):10.
According
to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), digestive diseases have affected more than 70 million Americans. More
than six million diagnostic and therapeutic procedures have been performed in
the more than 14 million people who have been hospitalized for digestive
diseases (14% of all inpatient procedures). Digestive diseases have cost in
excess of $120 billion, with $100 billion of this being direct medical costs.
Digestive diseases have disabled two million people and have led at least 45
million to seek ambulatory care.
Lactose intolerance, which has
the greatest prevalence of digestive diseases (about 50 million people), is
closely followed by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which
affects about 20% of the U.S. population. GERD has necessitated
hospitalization in more than 700,000 people, with an equal number of people
seeking ambulatory care, and it has caused disability in more than 45,000.
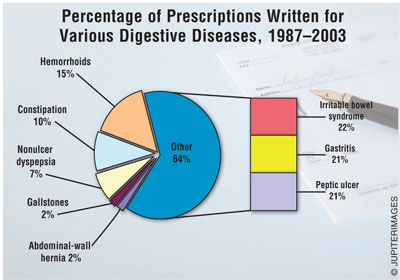
More than 20 million people
have gallstones, resulting in about 640,000 hospitalizations, roughly
two million ambulatory-care visits, more than one-half million surgical
procedures (cholecystectomy), and about 200,000 prescriptions.
Peptic ulcers are common; one
in 10 Americans develops one during his or her lifetime. Peptic ulcer has
affected about 15 million people, causing more than 400,000 to be hospitalized
and more than 875,000 million to seek ambulatory care. More than two million
prescriptions have been written for peptic ulcers.
Hemorrhoids are common in both
men and women; about half of the population develops them by age 50.
Hemorrhoids constitute the fifth most prevalent type of digestive disease (8.5
million people affected), with about two million ambulatory-care visits and
more than 1.5 million prescriptions written. About 170,000 people have been
hospitalized for hemorrhoids, which have a very low mortality rate (18 deaths
in 2002).
Abdominal-wall hernia has
affected more than 4.5 million people, necessitating ambulatory-care visits in
about 3.5 million and hospitalization in about 325,000. The condition has
caused disability in approximately 470,000 people, and at least 185,000
prescriptions have been written for it.
Gastritis is not a single
disease, but rather several different conditions involving inflammation of the
stomach lining. More than four million people suffer from gastritis, and in
excess of three million have had ambulatory care. Of the more than 6.5 million
people suffering from persistent indigestion or nonulcer dyspepsia (NUD), only
about 800,000 have had ambulatory care. According to the NIDDK, disability
caused by NUD is more than double that of gastritis (30,000), but the number
of prescriptions (two million) written for gastritis is three times that for
NUD.
One in five adults in the
United States has symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), making it one of
the most commonly diagnosed disorders. IBS occurs more often in women than in
men, and it begins before age 35 in about 50% of people. According to the
NIDDK, the number of prescriptions written for constipation is half (one
million) the number written for IBS, even though more than three million and
two million people, respectively, suffer from constipation and IBS. The number
of ambulatory-care visits for the treatment of constipation is more than three
million, versus more than two million for IBS.
To comment on this article,
contact rdavidson@jobson.com.





