US Pharm. 2012;37(2):8.
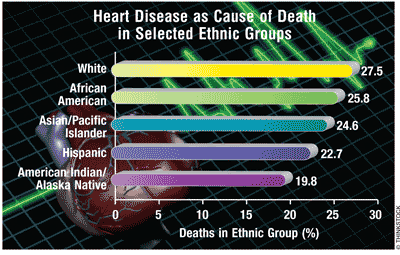
The 2010 National Health Interview Survey attributed 26% of all deaths to heart disease (HD), with coronary HD being the most common (70%). HD is a leading cause of death in people of most racial/ethnic groups, including African Americans, American Indians/Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and whites. Risk factors for HD, present in 90% of HD patients, include high cholesterol (HC), high blood pressure (HBP), diabetes, cigarette smoking, obesity, and physical inactivity during leisure.
Cigarette Smoking: There are 46 million smokers in the United States. In 2009, 23.5% and 17.9% of adult men and women, respectively, smoked. American Indians/Alaska Natives (23.2%) topped the list, followed by non-Hispanic whites (22.1%) and non-Hispanic blacks (21.3%); Hispanics (14.5%) were a distant fourth.
Diabetes: About 25.6 million U.S. adults have diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes, including 1.9 million newly diagnosed in 2010. About 7.1% of non-Hispanic whites, 8.4% of Asian Americans, 11.8% of Hispanics, and 12.6% of non-Hispanic blacks had diagnosed diabetes. Among Hispanics, rates were 7.6% for Cuban Americans and Central and South Americans, 13.3% for Mexican Americans, and 13.8% for Puerto Ricans. Compared with non-Hispanic white adults, the risk of diagnosed diabetes was 18% higher in Asian Americans, 66% higher in Hispanics, and 77% higher in non-Hispanic blacks. Compared with non-Hispanic whites, the risk of diagnosed diabetes was similar for Cuban Americans and Central and South Americans, 87% higher for Mexican Americans, and 94% higher for Puerto Ricans.
HC: This condition doubles the risk of HD. In the last 40 years, the prevalence of HC among adults dropped significantly from 33% (1960-1962) to 16.3% (2003-2006), but in 2010 more women (16.9%) than men (15.6%) had HC. White women (17.9%) had the highest prevalence, followed by Mexican American men (17.7%), white men (16%), Mexican American women (13.8%), African American women (13%), and African American men (11.2%).
HBP: Affecting 31.3% of adults in 2010, HBP is estimated to cost $76.6 billion. More than two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with HBP use medications to treat the condition, and HBP is controlled in 70% of those who take their medications as directed. Prehypertension occurs in 25% of adults. African Americans develop HBP at a greater rate than other ethnic groups.
Obesity: Nine states had an obesity rate of 30% or more in 2009 versus 12 states in 2010, with 33.8% of adults affected. Even more significantly, no state had an obesity rate of 30% or more in 2000. Non-Hispanic blacks have the highest rate of obesity (44.1%), followed by Mexican Americans (39.3%), all Hispanics (37.9%), and non-Hispanic whites (32.6%).
To comment on this article, contact rdavidson@uspharmacist.com.





